Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
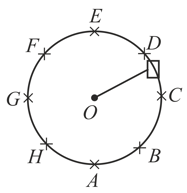
A machine, in an amusement park, consists of a cage of the end of one arm, hinged at . The cage revolves along a vertical circle of radius about its hinge , at constant linear speed . The cage is so attached that the man of weight standing on a weighing machine, inside the cage, is always vertical. Then which of the following is correct
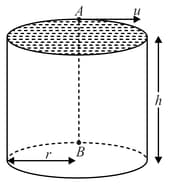
A hollow vertical cylinder of radius and height has a smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim, at point , and given a horizontal speed , tangential to the rim. It leaves the lower rim at point , vertically below . If is an integer then
A simple pendulum of length and mass (bob) is oscillating in a plane about a vertical line between angular limits and . For an angular displacement the tension in the string and velocity of the bob are and respectively. The following relations hold good under the above conditions
Which of the following process involve the transformation of energy from one form to another?
A particle is released from rest at the position . The potential energy graph of the particle is shown below:
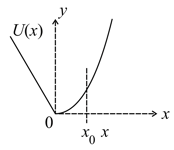
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
kinetic energy, potential energy, and work. Regarding expression
Which of the following is/are incorrect?
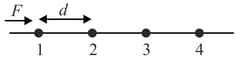
The diagram shows a string of equally placed beads of mass , separated by distance . The beads are free to slide without friction on a thin wire. A constant force acts on the first bead initially at rest till it makes collision with the second bead. The second bead then collides with the third and so on. Suppose that all collisions are elastic.
Two blocks and each of mass , are connected by a massless spring of natural length and spring constant . The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length, as shown in diagram. A third identical block , also of mass , moves on the floor with a speed along the line joining and , and collides elastically with . Then:-