Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 2: BEGINNER'S BOX - 2 with Hints & Solutions
Two blocks of masses and placed on a frictionless surface are connected by a spring. An external kick gives a velocity of to the heavier block in the direction of the lighter one. Calculate the velocity gained by the centre of mass.
Three particles of masses , and are subjected to forces , and respectively. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the centre of mass of the system.
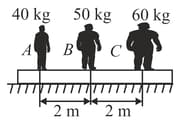
Three men and of masses and are standing on a plank of mass , which is kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If and exchange their positions then mass will shift
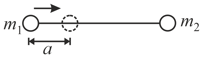
Consider a system having two masses and in which the first mass is pushed towards the centre of mass by a distance . The distance by which the second mass should be moved to keep the centre of mass at the same position is
Two particles and initially at rest, move towards each other under a mutual force of attraction. At the instant when the speed of is and the speed of is the speed of the centre of mass of the system is:-
The figure shows the positions and velocities of the two particles. If the particles move under the mutual attraction of each other, then the position of centre of mass at is

An isolated particle of mass is moving in a horizontal plane , along the -axis, at a certain height above the ground. It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses and . An instant later, the smaller fragment is at . The larger fragment at this instant is at
In which of the following cases, the centre of mass of a rod may be at its centre?
(1) The linear mass density decreases continuously from left to right.
(2) The linear mass density increases continuously from, left to right.
(3) The linear mass density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases.
(4) The linear mass density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
