Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: Exercise (Previous Year Questions)
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: Exercise (Previous Year Questions)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: Exercise (Previous Year Questions) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 4: Exercise (Previous Year Questions) with Hints & Solutions
A tube of length is filled completely with an incompressible liquid of mass and closed at both ends. The tube is then rotated in a horizontal plane about one of its ends with a uniform angular velocity . The force exerted by the liquid at the other end is
A car of mass negotiates a banked curve of radius on a frictionless road. If banking angle is , the maximum speed of car is
A car of mass is moving on a level circular track of radius . If represents the static friction between the road and tyres of the car, the maximum speed of the car in circular motion is given by
Two stones of masses and are whirled in horizontal circles, the heavier one in a radius and the lighter one in radius . The tangential speed of lighter stone is times that of the value of heavier stone when they experience the same centripetal force. The value of is,
A car is negotiating a curved road of radius . The road is banked at an angle . The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is . The maximum safe velocity on this road is
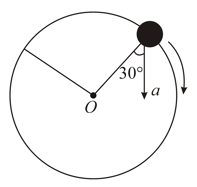
In the given figure, represents the total acceleration of a particle moving in the clockwise direction in a circle of radius at a given instant of time. The speed of the particle is
A particle starts with angular acceleration . It moves in a random interval of . Find out the time at which random interval starts.
One end of the string of length is connected to a particle of mass and the other end is connected to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in a circle with speed , the net force on the particle (directed towards the centre) will be ( represents the tension in the string)
