Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 8: Exercise (Analytical Questions)
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 8: Exercise (Analytical Questions)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 17: Thermodynamics, Exercise 8: Exercise (Analytical Questions) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 8: Exercise (Analytical Questions) with Hints & Solutions
A gas mixture contains and If the temperature of gas mixture is increased from to at isobaric process then find given heat of gas mixture:
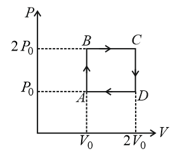
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle as shown in the figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is , the work done by the gas in the process is
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through a cycle as shown in the diagram. Column-II gives the characteristics involved in the cycle. Match them with each of the processes given in Column-I.
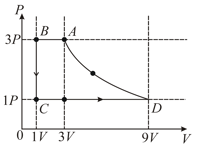
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Process | (p) Internal energy decreases |
| (B) Process | (q) Internal energy increases |
| (C) Process | (r) Heat is lost |
| (D) Process | (s) Heat is gained |
| (t) Work is done on the gas |
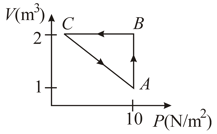
Three processes form a thermodynamic cycle as shown on diagram for an ideal gas. Process takes place at constant temperature (), Process takes place at constant volume, During this process of heat leaves the system. Process is adiabatic and temperature . Work done by the gas during the process is
The molar specific heat under constant pressure of oxygen is . The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature from moles of oxygen under constant volume will approximately will be
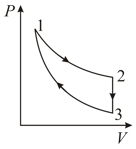
If the ratio of specific heats of a gas at constant pressure to that at constant volume is the change in internal energy of a gas when the volume changes from to at constant pressure is
The above P-V diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle is:
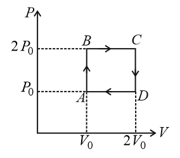
The P-V diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono atomic gas.