Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 1: Level 1
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 1: Level 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 22: Solutions, Exercise 1: Level 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 1: Level 1 with Hints & Solutions
The boiling point of aqueous solution of and should follow the order:
The freezing point of pure benzene is . When of butane is dissolved in of benzene, the freezing point of benzene decreases to . To lower the freezing point of benzene by another , the amount of butane that has to be added to mixture is:
The boiling points of two miscible liquids, which do not form an azeotropic mixture, are close to each other. Their separation is best carried out by:
The value of Henry's law constant of and in water at are and respectively. The order of their solubility in water at the same temperature and pressure is:
Upon mixing equal volumes of aqueous solutions of and the concentration of in the resulting solution is:
The variation of solubility of four different gases ( etc.,) in a given solvent with pressure at a constant temperature is shown in the plot.
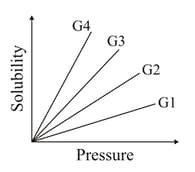
The gas with the highest value of Henry's law constant is
At the vapour pressure of two pure liquids, and are and , respectively. If in a mixture of and , the vapour pressure is , the mole fractions of in the liquid and in the vapour phase, respectively, are
At , the ratio of osmotic pressures of two solutions of a substance with concentrations of and , respectively, is:
