Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 3: Level 3
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 3: Level 3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 24: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 3: Level 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 3: Level 3 with Hints & Solutions
Assertion: Van der Waals equation describes the behaviour of real gases.
Reason: The kinetic theory postulates that negligible volume of gaseous molecules and intermolecular forces of attraction do not stand correct at high pressure and low temperature.
Van der Waals equation may be reduced to the following form:
This equation shows that (tick the incorrect one):
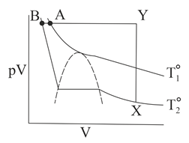
A gas at is condensed to a liquid, following the path . The liquid appears at the point:
The ratio between the velocity of at and that of at is
of gas effuses through a hole in a container in . The time taken for the effusion of the same volume of the gas specified below under identical conditions is
A sample of natural gas is of methane () and of ethane () by mass. What would be the density of this mixture at and ?
Answer by rounding off up to two places of decimals.
The vapour pressure of water at is . Calculate the mass of water (in mg) per litre of air at and relative humidity.
Answer correct up to two places of decimals.
The composition of the equilibrium mixture , which is attained at is determined by measuring the rate of effusion through a pinhole. It is observed that at pressure, the mixture effuses times as fast as krypton effuses under the same conditions. Calculate the fraction of chlorine molecules dissociated into atoms. (Atomic weight of )
Round off your answer up to two places of decimals.
