Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 2: Level 2
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 2: Level 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 3: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 2: Level 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 2: Level 2 with Hints & Solutions
The plot that is not valid for an ideal gas where is the pressure and is the volume of the gas is:
An ideal gas is subjected to a cyclic change as shown in the diagram below:
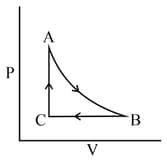
The step in which the gas will cool down is along:
Two balloons, and , containing mole and mole of helium at room temperature and ., respectively, are connected. When an equilibrium is established, the final pressure of in the system is:
At , assuming ideal behaviour, the average kinetic energy of a deuterium molecule is:
A specific volume of requires to diffuse out of a container. The time required by an equal volume of to diffuse out under identical conditions is:
The density of acetic acid vapor at and is . The number of acetic acid molecules in the cluster that is formed in the gas phase is the closest to
The volume vs. temperature graph of mole of an ideal gas is given below. The pressure of the gas (in ) at and , respectively, are

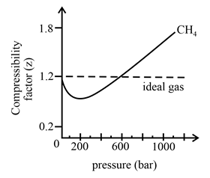
In the following compressibility factor vs. pressure graph at , the compressibility of at pressures deviates from ideal behaviour because: