Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 11: Ray Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Comprehensive Guide to AP EAPCET Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
A ray of light falls on a transparent glass slab of refractive index . If the reflected ray and the refracted ray are mutually perpendicular, the angle of incidence is
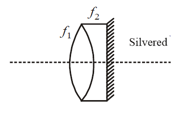
Two lenses of focal length and are kept as shown. The resultant power of combination will be
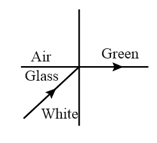
White light is incident on the interface of glass and air as shown in the figure. If the green light is just totally internally reflected then the emerging ray in the air contains
The frequency of a light wave in a material is and wavelength is . The refractive index of material will be
The refractive index for a prism is given as Then, angle of minimum deviation in terms of angle of the prism is
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index falls on a surface separating the medium from the air at an angle of incidence of For which of the following value of the ray can undergo total internal reflection?
The graph between angle of deviation and angle of incidence for a triangular prism is represented by
Diameter of a plano-convex lens is and thickness at the centre is . If speed of light in material of lens is the focal length of the lens is (Speed of light in vacuum =
