Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium & Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium & Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Chemical Equilibrium & Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Comprehensive Guide to BITSAT Chemistry. Other applicable Exams - JEE Main, BITSAT, SRM JEE, MHT-CET, K-CET, EAMCET, AMU & Other State Engg. Entrance Exams solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium & Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
Steam reacts with iron at high temperature to give hydrogen gas and The correct expression for the equilibrium constant is
The reaction is:
The reaction of hydrogen and iodine monochloride is given as:
The reaction is of a first-order, with respect to and following mechanisms were proposed.
Mechanism
Mechanism
slow
fast
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
;In the reversible reaction, the rate of disappearance of is equal to:
The reaction,
is begun with the concentrations of and both at an initial value of When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of is measured and found to be The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression:
The hypothetical reaction,
follows the following mechanism:
The order of the overall reaction is:
For the reaction system,
volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order with respect to and second order with respect to the rate of reaction will:
Consider the following reaction,
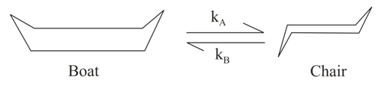
The reaction is of first order in each diagram, with an equilibrium constant of For the conversion of chair form to boat form at with pre-exponential factor of Apparent rate constant at is:
Acid hydrolysis of ester is a first order reaction and the rate constant is given by,
where, and are the volume of standard required to neutralise an acid present. At any given time, if ester is neutralised at time , then
