Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Compounds of Non - Metals, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2018
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Compounds of Non - Metals, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2018
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Compounds of Non - Metals, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2018 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR CHEMISTRY solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Compounds of Non - Metals, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2018 with Hints & Solutions
What is the total number of moles of reactants and products in the above reaction?
What is the effect of pressure in this reversible reaction? Explain.
Which are the chemicals used to prepare ammonia in the laboratory?
If we show a red litmus paper over ammonia gas, what changes can be observed?
If we show a red litmus paper over ammonia gas, it turns blue.
Which property of ammonia is shown here?
Graph of a reversible process;
is given. Analyse the graph and answer the following question.
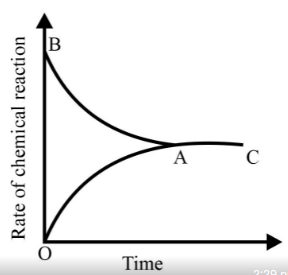
Identify the part of the graph which represents the forward reaction
[ OA, BA, AC]
Graph of a reversible process;
is given. Analyse the graph and answer the following question.
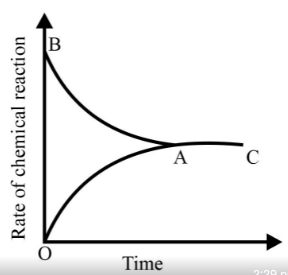
Identify the part of the graph which represents the equilibrium state?
Graph of a reversible process,
is given. Analyse the graph and answer the following question.
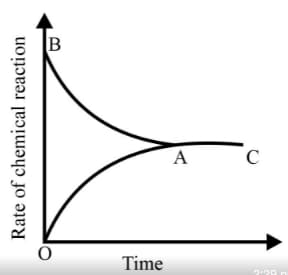
From the given statements, select the correct ones regarding chemical equilibrium.
(i0 The chemical equilibrium is 'static' at the molecular level.
(ii) Both reactants and products co-exist.
(iii) The rates of forward reaction and backward reactions are equal.
(iv) Chemical equilibrium is attained in an open system.
