Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2014
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2014
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 3: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2014 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR CHEMISTRY solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 1 - 2014 with Hints & Solutions
Liquids and form ideal solution for all compositions of and at . Two such solutions with and mole fractions of have the total vapor pressures of and bar, respectively. What is the vapor pressure of pure liquid in bar?
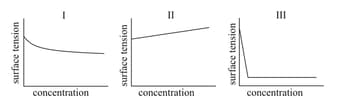
The qualitative sketches I, II and III given below show the variation of surface tension with molar concentration of three different aqueous solutions of KCl, and at room temperature. The correct assignment of the sketches is -
One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfied the equation where b is a constant. The relationship of interatomic potential V(r) and interatomic distance r for the gas is given by
In thermodynamics, the work done is given by . For a system undergoing a particular process, the work done is,
. This equation is applicable to a
Aluminium reacts with sulfuric acid to form aluminium sulfate and hydrogen. What is the volume of hydrogen gas in liters produced at and atm pressure, when of aluminium and of sulfuric acid are combined for the reaction? (Use molar mass of aluminium as , )
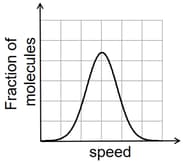
If the distribution of molecular speeds of a gas is as per the figure shown below, then the ratio of the most probable, the average, and the root mean square speeds, respectively, is
Which of the following statement(s) (are) correct regarding the root-mean-square speed and average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas at equilibrium?
