Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 1: BITSAT 2017
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 1: BITSAT 2017
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Kinematics, Exercise 1: BITSAT 2017 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 1: BITSAT 2017 with Hints & Solutions
A projectile is given an initial velocity of where is along the ground and is along the vertical. Then, the equation of the path of projectile is Take,
Consider the acceleration, velocity and displacement of a tennis ball as its falls to the ground and bounces back. Directions of which of these change in the process?
A stone is projected with velocity , so that it just clears two walls of equal height , at distance of from each other. The time interval of passing between the two walls is
A ball is dropped vertically from a height above the ground. It hits the ground and bounces up vertically to a height Neglecting subsequent motion and air resistance, its velocity varies with height above the ground as
An aeroplane is flying in a horizontal direction with a velocity and at a height of . When it is vertically below a point on the ground a food packet is released from it. The packet strikes the ground at point . If and , then the value of is
The horizontal range and maximum height attained by a projectile are and respectively. If a constant horizontal acceleration is imparted to the projectile due to wind, then its horizontal range and maximum height will be
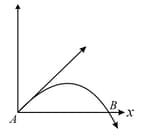
The velocity of a projectile at the initial point is . Its velocity (in ) at point is
A particle moving along -axis has acceleration , at time given by, where and are constants. The particle at and the instant when , the particle's velocity is
