Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2019
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2019
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2019 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Kerala Board-2019 with Hints & Solutions
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length and an eyepiece of focal length . What is the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when the telescope is in normal adjustment.
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length and an eyepiece of focal length . What is the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a spherical mirror falls at a point as shown in the figure below:
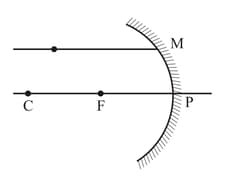
Identify the type of mirror used in the diagram.
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a spherical mirror falls at a point as shown in the figure below:
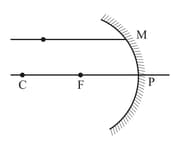
By drawing a suitable ray diagram, obtain the mirror equation.
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a spherical mirror falls at a point as shown in the figure below:
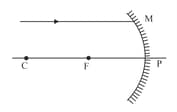
If the mirror is immersed in water, its focal length _____.
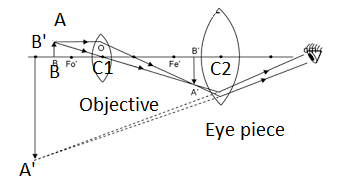
The figure shows the image formation of an object in simple microscope. Find out the object distance and image distance from the figure.
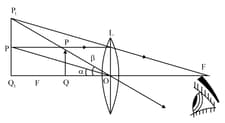
The figure shows the image formation of an object in simple microscope.
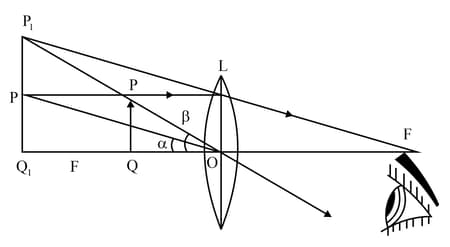
Derive an equation for magnifying power of the simple microscope.
A long narrow slit is illuminated by blue light and the diffraction pattern is obtained on a white screen.
What do you mean by limit of resolution of an optical instrument ?
