Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 17: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: AIPMT - 4th May 2014 with Hints & Solutions
A light ray falls on a glass surface of refractive index , at an angle . The angle between the refracted and reflected rays would be:
A biconvex lens has radii of curvature each. If the refractive index of the material of the lens is , the power of the lens is:
Two transparent media and are separated by a plane boundary. The speed of light in those media are and , respectively. The critical angle for a ray of light for these two media is:
A convex lens of focal length and a concave lens of focal length are kept along the same axis with a distance between them. If a parallel beam of light falling on leaves as a parallel beam, then the distance in will be :
A lens of large focal length and large aperture is best suited as an objective of an astronomical telescope since:
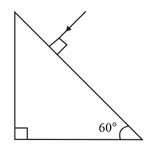
Find the value of the angle of emergence from the prism. Refractive index of the glass is .
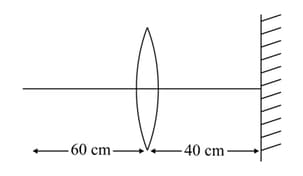
A point object is placed at a distance of from a convex lens of focal length . If a plane mirror were put perpendicular to the principal axis of the lens and at a distance of from it, the final image would be formed at a distance of :
The power of a biconvex lens is dioptre and the radius of curvature of each surface is Then the refractive index of the material of the lens is,
