Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: SAT 2019
Embibe Experts Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: SAT 2019
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 1: SAT 2019 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR SAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: SAT 2019 with Hints & Solutions
Suppose that the acceleration versus time graph of a particle that starts from rest at is as shown in the figure.
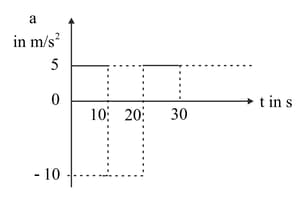
At what instant does the particle come to rest for the first time?
Suppose that the acceleration versus time graph of a particle that starts from rest at is as shown in the figure.
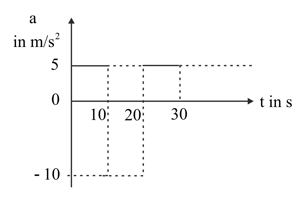
What is the total distance travelled by the particle during ?
Two identical objects A and B each of mass m start moving along the same vertical line in opposite directions at the same instant. Object A is dropped from rest from a height H above the ground and object B is projected vertically upward from the ground with speed . At what height above the ground do they collide?
Two identical objects A and B each of mass m start moving along the same vertical line in opposite directions at the same instant. Object A is dropped from rest from a height H above the ground and object B is projected vertically upward from the ground with speed . After they collide, they stick to each other. What is the loss in their total energy?
Figures given below show velocity – time curves for a moving object. Identify the one which may be realised in practice.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards at a speed and returns to the thrower. There are two instants at which the ball has equal kinetic and potential energies. The difference between these two instants is
A car P is moving with a uniform speed towards another car Q at rest on a straight level road. At a particular instance when the distance between P and Q is the car Q started accelerating at towards P. Find the distance travelled by Q, when both the cars meet.
A body travels the distance with a speed . Thereafter, it travels with speed and the remaining with . Calculate the average speed for this journey assuming that the body takes the same time in travelling distances and .