Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course (Based on Revised Syllabus-2023) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
Calculate the energy of charged parallel plate capacitor. Express the energy in terms of electric field. Now calculate the energy density. Can this result be generalised ?
An elementary particle of mass m and charge +e initially at very large distance is projected with velocity v at a much more massive particle +Ze at rest. The closest possible distance of approach of the incident particle is
What are meant by equipotential surfaces?
A sphere of radius has positive charge uniformly distributed on its surface. A small pellet of mass and charge is directed radially at the sphere. When the pellet is at a distance of 0.75 m from the centre of the sphere its speed is .
Determine the distance from the centre of the sphere at which the pellet will stop.
A parallel plate air capacitor has capacitance It is charged by connecting to a battery. Then it is disconnected from the battery and the space between the two plates of the capacitor is filled with a material having dielectric constant Compare
capacitance,
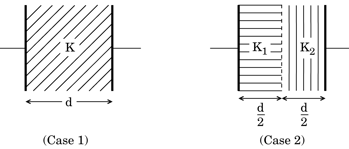
The space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is completely filled in two ways. In the first case, it is filled with a slab of dielectric constant . In the second case, it is filled with two slabs of equal thickness and dielectric constants and respectively as shown in the figure. The capacitance of the capacitor is same in the two cases. Obtain the relationship between , and .
Explain the behaviour of dielectrics in an external field.
If electric potential at a point is zero then electric field intensity must be zero.Give reasons with an example.
