Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course (Based on Revised Syllabus-2023) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror. It is observed that a virtual image is formed. Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation and hence derive the mirror equation .
An object is placed at a distance from the pole of a convex mirror of the focal length of . Calculate the linear magnification of the mirror.
Define the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror?
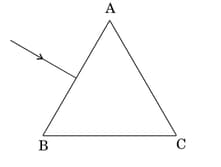
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having a refractive index , placed in water of refractive index . Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
What are the different types of beam of lights?
Define aperture and angular aperture.
Show the formation of image in a concave mirror through a ray diagram and derive the lens equation.
What are non paraxial rays?
