Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Properties of Solid and Liquid, Exercise 2: Level 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Properties of Solid and Liquid, Exercise 2: Level 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Properties of Solid and Liquid, Exercise 2: Level 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Properties of Solid and Liquid, Exercise 2: Level 2 with Hints & Solutions
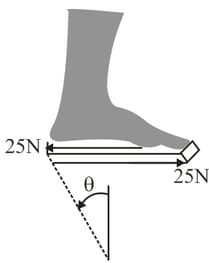
As a runner's foot pushes off the ground, the shear force acting on a thick sole, is shown in the diagram. If the force of is distributed over the area of the angle of shear (in degrees) is: (Given that shear modulus of the sole is ) (Approximate the answer to the nearest integer.)
A cube made of homogeneous material is kept on a horizontal surface. What is the ratio of strain energy stored in lower one third to the upper one third of the cube?
(Write answer as an integer)
A steel wire of cross-sectional area can withstand a maximum strain of . Young's modulus of steel is . The maximum mass this wire can hold is,
One end of a slack wire (Young's modulus , length and cross-sectional area ) is clamped to a rigid wall and the other end to a block (mass ) which rests on a smooth horizontal plane. The block is se in motion with a speed . What is the maximum distance the block will travel after the wire becomes taut?
An elastic spring has a force constant . It is cut into three equal parts. The force constant of each part is
A block of wood has a mass of When a metal piece with volume of is attached to the bottom of the block, the wood barely floats in water. What is the volume of the wood?
A long capillary tube of mass radius and negligible thickness, is partially immersed in a liquid of surface tension Take angle of contact zero and neglect the buoyant force of liquid. The force required to hold the tube vertically is newton. Find
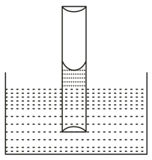
A solid ball is falling through a viscous liquid of viscosity It has a terminal speed of Now we take another solid ball of same material but radius twice the first ball falling through same liquid, what is the new terminal speed (in )?
