Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 16: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
A straight current carrying conductor is placed in such a way that the current in the conductor flows in the direction out of the plane of the paper. The conductor is placed between two poles of two magnets, as shown
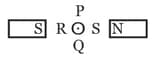
The conductor will experience a force in the direction towards
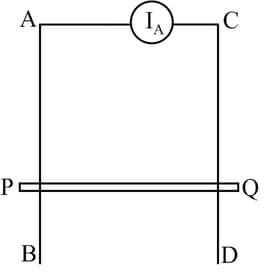
and are fixed conducting smooth rails placed in a vertical plane and joined by a constant current source at its upper end. is a conducting rod which is free to slide on the rails. A horizontal uniform magnetic field exists in space as shown. If the rod is released from rest then,
The current sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer of resistance is Its voltage sensitivity is
An ammeter and a milliammeter are converted from identical galvanometers. Which one has smaller resistance?
Sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer can be increased by:
In an attempt to increases the current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer, it is found that its resistance becomes double while the current sensitivity increases by . The voltage sensitivity of the galvanometer changes by
If the number of turns and radius of cross section of the coil of a tangent galvanometer are doubled, then the reduction factor will become
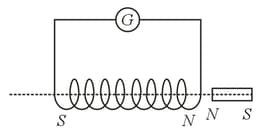
A short bar magnet passes at a steady speed right through a long solenoid. A galvanometer is connected across the solenoid. Which graph best represents the variation of the galvanometer deflection with time