Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1 with Hints & Solutions
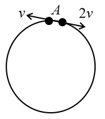
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities fare and , respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move at constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at , these two particles will again reach the point
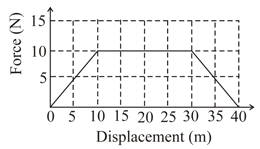
Adjacent figure shows the force-displacement graph of a moving body, the work done in displacing body from to is equal to
Which of the following graphs is correct between kinetic energy potential energy and height from the ground of the particle ( and at )
With how much velocity a block of mass move on a frictionless surface so as to compress a spring with force constant newton/metre by metres.
For a two particle collision, the following quantities are conserved in general-
A car of mass is driven with acceleration along a straight level road against a constant external resistive force When the velocity of the car is the rate at which the engine of the car is doing work will be
A train weighing is running on a level track with uniform speed of the frictional force is per quintal. What is the power of the engine-
An engine pumps up of water through a height of in Given that the efficiency of the engine is If the power of this engine is:
