Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Periodic Classification of Elements, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Science Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Periodic Classification of Elements, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Periodic Classification of Elements, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. THINK ABOVE AND BEYOND SCIENCE PRACTICE BOOKS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Periodic Classification of Elements, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
Rajveer and Neha are preparing for a competitive exam. They were studying together the topic of ionic compounds and the formation of ionic compounds.

While studying they found one problem in which a metal '' with an atomic number is given.
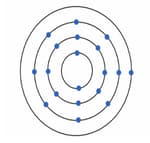
It burns with chlorine having an atomic number to produce a white solid chloride ''.
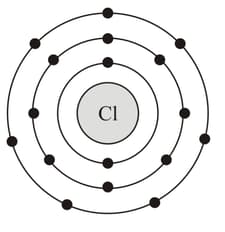
Help them to deduce the name of Metal ''. Also, show the diagrams depicting the arrangement of electrons in '' after the reaction takes place.
A teacher completed the chapter on the Periodic classification of elements. She has given a chart of Mendeleev's Periodic table to Raju and asked the following questions:
(a) Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his Periodic Table?
(b) How did Mendeleev named the elements that fit in the empty spaces given in the group and the group of his periodic table?
(c) What names were given to these elements when these elements were discovered later on?
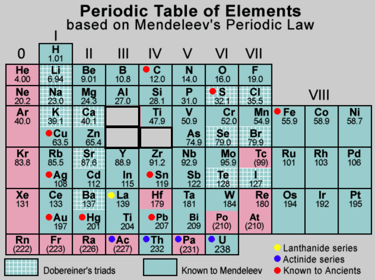
Can you help Raju to solve these questions?
We all have a particular address for our residence. Similarly, for every element, a position is given in the modern periodic table.
A teacher in a school gave some clues about an unknown element to Rahul and informed him to find out the exact location of the element in the periodic table. The clues given are as follows:
- The element has electrons in its outermost shell.
- It is a gaseous element.
- It has the ability to attract electrons towards itself.
- It has nucleons.
Can you help Rahul to trace the location of the given element?
A teacher has given a chart containing some elements having atomic numbers to to Rahul. The table contains elements which were represented by certain letters of the alphabet (these letters are not the usual symbols of these elements):
She asked some questions to Rahul. Using the above table, can you help Rahul to solve the following questions?
(i) Which of these is a halogen?
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed when reacts with .
A teacher discussed about the origin of classification of elements and Dobereiner's triads in the classroom. Teacher then assigned an assignment to Raju. Can you help Raju to solve the following question?
P, Q and R are the elements of a Dobereiner's triad. What should be the atomic mass of Q, if the atomic number of P is and number of neutrons in its nucleus are , also the atomic number of R is . Find out the element Q.
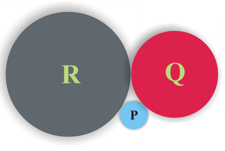
Rutherford carried out a fairly simple calculation to find the size of the nucleus, and found it to be only about the size of the atom. Around the nucleus there are various energy levels at some distances from the nucleus one after other where electrons are supposed to rotate. These imaginary circular paths are called orbits. To measure the size of an atom if an atom is supposed to be a sphere, scientists approximated that the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost orbit is the size of the atom which is roughly a radius of the sphere.
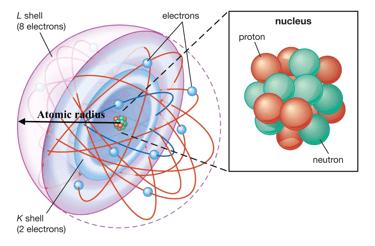
Every atom present in the modern periodic table has different atomic size and periodic table could help compare the sizes of different atoms. Hydrogen is the smallest atom and Francium has the greatest atomic size in the periodic table.

- There are four elements . Give the ascending order of atomic size.
The modern or long form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law. The table is the arrangement of elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers. The modern periodic table is the present form of the periodic table. And it consists of vertical columns and horizontal rows.
The teacher took a lesson on the modern periodic table in the classroom. One table with some information is already given to students. And she asked them to answer the following questions.

| Group 15 | Group 16 | Group 17 |
| D | __ | A |
| __ | B | C |
Elements A, B, C and D belong to groups of the periodic table as shown in the table above.
(i) Is C a metal or non-metal?
(ii) Which is more reactive, C or A?
(iii) Which will be smaller, B or C?
(iv) Name the family to which A belongs.
(v) What is the valency of B.
(vi) The formula of the delta formed between D and C.
Classification of things makes it easier to organise, identify or study them. Since a long time ago the known elements were classified into metals and non-metals. The discoveries of new elements expanded the perception of the scientists that not all metals or non-metals possess the same property. Every metal is different from the other in some way or the other. Though their physical properties are the same, but chemical properties are not the same and vice versa. It was then tough to study the properties of every element.
There were few scientists named Dobereiner, Lothar Meyer and Newlands who attempted to classify the elements. It was clear from their attempts that elements show periodicity in their properties. Periodicity is the term used for the repeating of something after particular intervals. On Mendeleev began arranging the elements and comparing them by their atomic weights and arranged them in a tabular representation which proposed the idea of the first periodic table of elements. The modern periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements and is organised on the basis of their atomic numbers. The law of periodicity that is related to atomic numbers was proposed by Henry Moseley.

Rupali has been provided with five elements A, B, C, D and E with atomic numbers and and Aviral with five elements P, Q, R, S and T with atomic numbers and .
Find out the pairs of elements from the two groups of elements that will exhibit similar chemical properties.
