Magnet
Important Questions on Magnet
How can an animal recognise the earth's magnetic field?
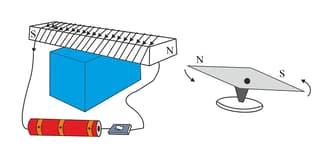
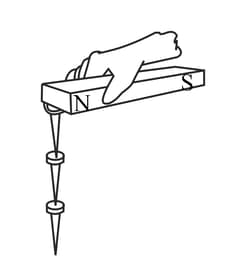
Take an iron bar, a long insulated electrical wire, a switch, a powerful battery, and a magnetic needle. Coil the wire around the iron bar as shown in the figure. Connect the two ends of the wire to the two ends of the battery through a switch (as shown in the picture). Now bring a magnetic needle near the iron bar and switch on the circuit. Try to understand what kind of pole has been created at the end of the iron bar nearer to the needle. Now interchange the two ends of the wire that are attached to the battery. Repeat the experiment once again, and observe which end of the needle is attracted (or repelled) by which end of the iron bar. Does the iron bar become a magnet when electricity is passed through the coil?
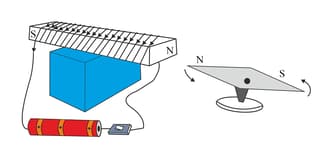
Take an iron bar, a long insulated electrical wire, a switch, a powerful battery, and a magnetic needle. Coil the wire around the iron bar as shown in the figure. Connect the two ends of the wire to the two ends of the battery through a switch (as shown in the picture). Now bring a magnetic needle near the iron bar and switch on the circuit. Try to understand what kind of pole has been created at the end of the iron bar nearer to the needle. Now interchange the two ends of the wire that are attached to the battery. Repeat the experiment once again, and observe which end of the needle is attracted (or repelled) by which end of the iron bar. Now stop the current flowing through the circuit. Why does the needle come back to its original position?
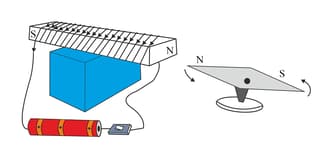
Take an iron bar, a long insulated electrical wire, a switch, a powerful battery, and a magnetic needle. Coil the wire around the iron bar as shown in the figure. Connect the two ends of the wire to the two ends of the battery through a switch (as shown in the picture). Now bring a magnetic needle near the iron bar and switch on the circuit. Try to understand what kind of pole has been created at the end of the iron bar nearer to the needle. Now interchange the two ends of the wire that are attached to the battery. Repeat the experiment once again, and observe which end of the needle is attracted (or repelled) by which end of the iron bar. Why does the needle deflect? Which external body applies a force upon the poles of the needle?
Is there any other magnet near it that influences the suspended magnet? Earth itself is that magnet?
Why does a suspended magnet point towards the North-South direction even when there is no other magnet near it?
Do you know under which influence does the suspended magnet change its direction?
A suspended bar magnet points north-south. If a friend of yours approaches it with another magnet in his pocket, what will happen? Will the suspended magnet still point towards north-south?
Could you separate the two poles of the magnet?
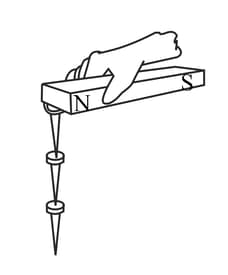
Take several nails and see whether you can make a chain of hanging nails. Now carefully hold the first nail (in direct contact with the magnet) take care so that no nail falls from the chain. Slowly take away the magnet. What can you see? Why do the nails fall?
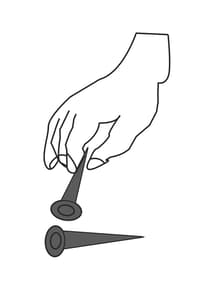
In the above picture, is the first nail attracting the second nail? Why?
Hold the bar magnet as shown in the figure. Touch a nail to one of its poles and allow it to cling to the magnet. Touch another nail to the first one and leave it. What can you see? Why is the second nail hanging from the first one? Why is it not falling?
Touch a nail with another shown in the below picture. Do they attract each other?
Between attraction and repulsion, which one is the surest experiment of a magnet?
Bring the pole 'N' of the magnet held in your hand near the pole 'S' of the suspended magnet. What do you see now? Do the two opposite poles still attract each other?
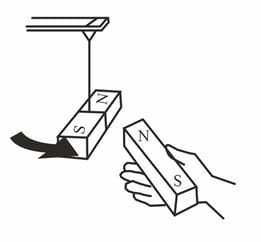
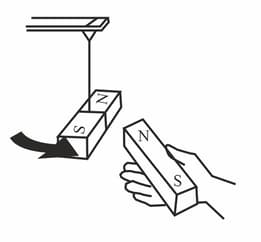
Is there any force acting between the two opposite poles? Is it attractive or repulsive?
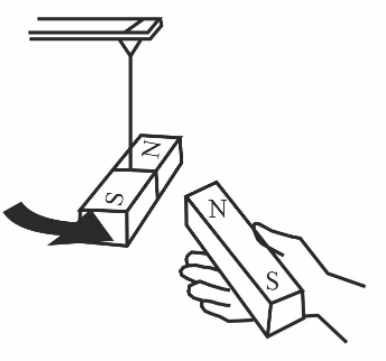
Why is the pole 'S' of the suspended magnet attracted towards the pole 'N' of the magnet held in the above picture?
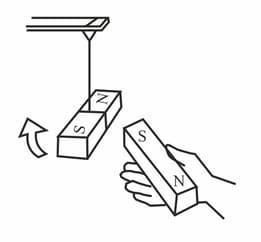
Take the south pole (S) of the magnet held in your hand near the pole of the suspended magnet. What can you see?
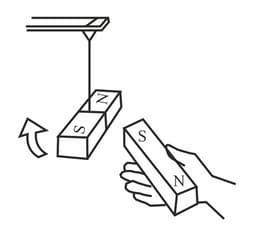
Suspend a bar magnet by a thread or other way, as shown in the figure. Take care that no other magnet or magnetic material is in the vicinity of that magnet. Now take the south pole of the magnet held in your hand near the south pole of the hanging magnet at equilibrium. What could you see this time? What conclusion can be reached from this observation?
Suspend a bar magnet by a thread or other way, as shown in the figure. Take care that no other magnet or magnetic material is in the vicinity of that magnet. Allow the magnet to come to equilibrium. Now take the north pole (N) of another magnet near it. Has the north pole of the second magnet applied the force on the first magnet?

