GMAC Solutions for Chapter: Logical Reasoning, Exercise 4: Practice Questions
GMAC Logical Reasoning Solutions for Exercise - GMAC Solutions for Chapter: Logical Reasoning, Exercise 4: Practice Questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 1: Logical Reasoning, Exercise 4: Practice Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NMAT Official Guide 2020 - Logical Reasoning solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from GMAC Solutions for Chapter: Logical Reasoning, Exercise 4: Practice Questions with Hints & Solutions
In each of the following questions, the three given words are related in one of the five ways represented by the diagrams given below. Choose the correct diagram which depicts the exact relation among the objects.
Grandmother, Mother, Girls:
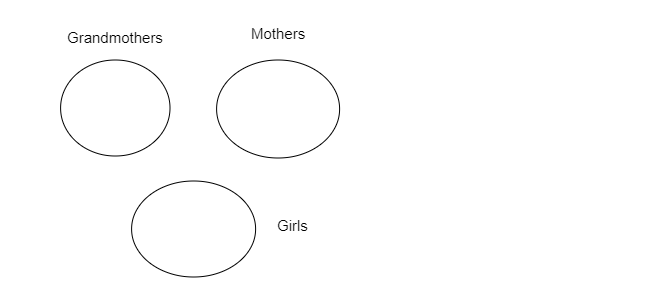
In each of the following questions, the three given words are related in one of the five ways represented by the diagrams given below. Choose the correct diagram which depicts the exact relation among the objects.
Children, Humans, Animals:
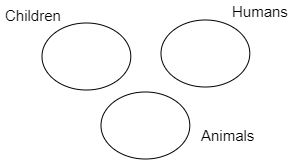
In each of the questions below, three statements are followed by three or four conclusions. Decide which of the given conclusion(s) logically follow(s) from the given statements, and hence is/are true.
Statements:
(1) Some print are wrong.
(2) All wrong are deform.
(3) No deform are right.
Conclusion I Some print are deform.
Conclusion II Some print are right.
Conclusion III Some deform are wrong.
Conclusion IV All deform are wrong.
In each of the questions/set of questions below, statements are given followed by the conclusions numbered accordingly. You have to assume all the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the information given in the statements. Give answer.
Statements:
(1) All ships are goats.
(2) All goats are cows.
(3) No goat is a horse.
Conclusion I: Some horses are cows.
Conclusion II: No horse is a cow.
In each of the questions/set of questions below, statements are given followed by the conclusions numbered accordingly. You have to assume all the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the information given in the statements. Give answer.
Statements:
(1) Some stones are rocks.
(2) Some rocks are rings.
Conclusion I: Some stones are rings.
Conclusion II: Some rocks are stones.
In each of the questions/set of questions below, statements are given followed by the conclusions numbered accordingly. You have to assume all the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the information given in the statements. Give answer.
Statements:
(1) Some grapes are strawberries.
(2) All strawberries are oranges.
(3) Some oranges are apples.
Conclusion I: All strawberries are apples.
Conclusion II: Some grapes are not strawberries.
In each of the questions/set of questions below, statements are given followed by the conclusions numbered accordingly. You have to assume all the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the information given in the statements. Give answer.
Statements:
(1) All sheep are goats.
(2) Some goats are dogs.
(3) All cats are dogs.
Conclusion I: No cat is a sheep.
Conclusion II: Some cats are goats.
In each of the questions/set of questions below, statements are given followed by the conclusions numbered accordingly. You have to assume all the statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the information given in the statements. Give answer.
Statements:
(1) No desk is a room.
(2) Some desks are halls.
Conclusion I: Some halls are definitely not desks.
Conclusion II: No room is a hall
