B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 6: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Electrostatics and Current Electricity JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: DPP with Hints & Solutions
and resistors are connected in series. This connection is connected with a battery of . When a voltmeter of resistance is connected across resistor, then the reading of the voltmeter will be
An ammeter gives a full-scale deflection when a current of is passed in it. To convert it into a range ammeter, the ratio of its resistance and the shunt resistance will be
current gives a full-scale deflection in a galvanometer of resistance. The resistance connected with the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter to measure is
When a resistor is connected with a moving coil galvanometer, then its deflection reduces from divisions to divisions. The resistance of the galvanometer is
A voltmeter has a range with a series resistance . With a series resistance , the range is . The correct relation between and is
A moving coil galvanometer is converted into an ammeter reading up to , by connecting a shunt of resistance across it, and into an ammeter reading up to , when a shunt of resistance is connected across it. What is the maximum current which can be sent through this galvanometer, if no shunt is used?
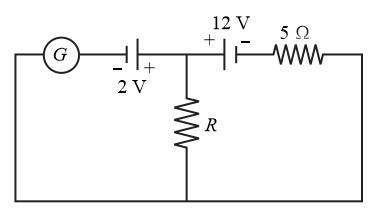
In the circuit shown, the galvanometer shows zero current. The value of resistance is
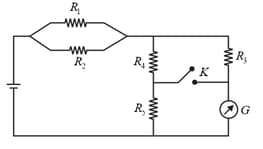
Whether the switch is open or closed, the reading of galvanometer is the same. If denotes the current in respective resistance, then