Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Work and Energy, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course BITSAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work and Energy, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
An ideal spring is used to fire a block horizontally across a frictionless table top. The spring has a spring constant of and is initially compressed by The speed of the block as it leaves the spring is
A block attached to an ideal spring with a spring constant of oscillates on a horizontal frictionless surface. When the spring is shorter than its equilibrium length, the speed of the block is The greatest speed of the block is
A simple pendulum consists of a mass attached to a string. It is released from rest at as shown. Its speed at the lowest point is
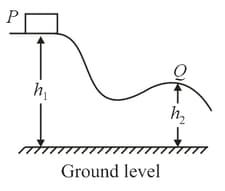
A block is released from rest at point and slides along the frictionless track shown. At point its speed is
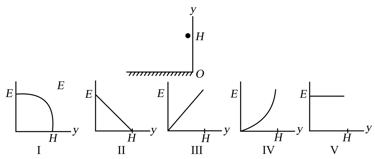
A ball is held at a height above a floor. It is then released and falls to the floor. If air resistance can be ignored, which of the five graphs below correctly gives the mechanical energy of the Earth-ball system as a function of the altitude of the ball?
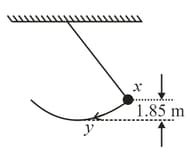
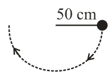
The string in the figure is long. When the ball is released from rest, it will swing along the dotted arc. How fast, in will it be going at the lowest point in its swing?
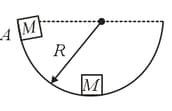
When a block of mass is released from point on the surface of a smooth bowl, the normal reaction force on it at the lowest point would be equal to
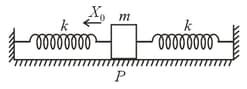
In the spring mass system shown in the figure, the spring is compressed by from its natural length and the block is released from rest. The speed of the block, when it passes through the point at means position, is