Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum
Important Questions on Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum
Two balls, having linear momenta and , undergo a collision in free space. There is no external force acting on the balls. Let and be their final momenta. The following option (s) is (are) not allowed for any non-zero value of and :
Two particles of masses and in projectile motion have velocities and respectively at time . They collide at time . Their velocities become and at time , while still moving in the air. The value of is:
A particle moves in the x-y plane under the action of a force such that the value of its linear momentum at any time is . The angle between and at a given time will be:
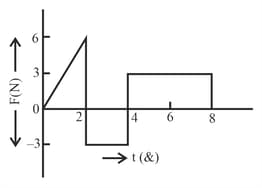
The force acting on a particle of mass is indicated by the force-time graph shown adjoining. The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from is:
A balloon of mass is descending down with an acceleration . How much mass should be removed from it so that it starts moving up with an acceleration ?
An isolated particle of mass is moving in a horizontal plane along the , at a certain height above the ground. It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses and . An instant later, the smaller fragment is at . The larger fragment at this instant is at:
A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity of at an angle with the horizontal. It explodes into two pieces of equal masses at the highest point of its path. One of the pieces retraces its path to cannon. The speed of the other piece immediately after the explosion is:
A body of mass is lying in plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces, each of mass move perpendicular to each other with equal speeds . The kinetic energy generated due to the explosion is:
A ball falls vertically on a surface at a speed of and rebounds with the same speed. The ball remains in contact with the surface for . The average force exerted by the surface on the ball is:
Sand is being dropped on a conveyor belt at the rate of . The force necessary to keep the belt moving with a constant velocity of will be:
Consider a car moving on a straight road with a speed of . The distance at which the car can be stopped is ,
An empty car is moving with velocity on a smooth road can be stopped in a distance by applying brakes. If the passengers add to its weight and the braking force remains the same, the stopping distance for the same velocity is:
Based upon the following paragraph answer the following multiple choice question:
Paragraph:
Phase space diagrams are useful tools for analyzing all kinds of dynamical problems. They are especially useful in studying the changes in motion as initial position and momentum are changed. Here we consider some simple dynamical systems in one dimension. For such systems, phase space is a plane, in which position is plotted along the horizontal axis and momentum is plotted along the vertical axis. The phase space diagram is vs. curve in this plane. The arrow on the curve indicates the time flow. For example, the phase space diagram for a particle moving with constant velocity in a straight line as shown in the figure. We use the sign convention in which opposition and momentum upwards(or to right) are positive and downwards (or to left) are negative.
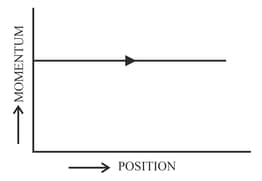
The phase space diagram for a ball thrown in the vertically upward direction is:
The mass of a rocket is . Its engine exerts on it an initial thrust of in the upward direction. Calculate the initial acceleration attained by the rocket.
In a rocket, the mass of the fuel is of the total mass. The exhaust gases are ejected at a speed of . Find the maximum speed attained by the rocket. Neglect gravity and air resistance and take the initial speed of the rocket to be zero. Given :
In a rocket fuel is burnt at the rate of and burnt gases rush at a speed of . Find the thrust of the rocket ignoring gravity.
A metallic block of mass is resting on a frictionless plane. It is struck by a jet releasing water at a rate of and at a speed of . Find the initial acceleration of the block.
The velocities of two bodies(masses and ) in the and the directions are and respectively. They collide and stick together. What is the final velocity?

