Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: EXERCISE 11.1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: EXERCISE 11.1
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 1: EXERCISE 11.1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Exercise 1: EXERCISE 11.1 with Hints & Solutions
The momentum of a photon is . Its frequency will be
A metal surface of work function is irradiated with light of wavelength . The retarding potential required to stop the escape of photo-electrons is
Ultraviolet radiation of falls on an aluminium surface (work function ). The kinetic energy in joule of the fastest electron emitted is approximately-
The work function for tungsten and sodium are and respectively. If the threshold wavelength for sodium is , the value of for tungsten is
The work function of a metallic surface is The photo-electrons are emitted when the light of wavelength falls on it. The potential difference applied to stop the fastest photo-electrons is
A metal surface is illuminated by the light of two different wavelengths and . The maximum speeds of the photoelectrons corresponding to these wavelengths are and , respectively. If the ratio and , the work function of the metal is nearly
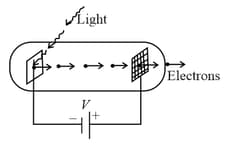
Light of wavelength falls on a cathode plate inside a vacuum tube as shown in the figure. The work function of the cathode surface is and the anode is a wire mesh of conducting material kept at a distance from the cathode. A potential difference is maintained between the electrodes. If the minimum de-Broglie wavelength of the electrons passing through the anode is , which of the following statement is true?
An -particle and a proton are accelerated from rest by a potential difference of . After this, their de-Broglie wavelengths are and , respectively. The ratio to the nearest integer is
