K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 5: Test yourself
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 5: Test yourself
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 5: Test yourself with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Wave Phenomena (HL), Exercise 5: Test yourself with Hints & Solutions
Explain, with the help of diagrams, the Doppler's effect. Shows clearly the cases of source that
a. Moves towards and
b. Goes away from a stationary observer.
A source of sound is directed at an approaching car. The sound is reflected by the car and is received back at the source. Carefully explain what changes in frequency the observer at the source will detect.
A sound wave of frequency is emitted by a stationary source towards a receding observer. The signal is reflected by the observer and received by the source, where the frequency is measured and found to be . Calculate the speed of the observer.
A sound wave of frequency is emitted by a moving source towards a stationary observer. The signal is reflected by the observer and received by the source, where the frequency is measured and found to be . Calculate the speed of the source.
Consider a general case when both the source and the observer move towards each other. Let be the velocity of the source and that of the observer. In the frame of reference in which the observer is at rest, the waves appear to move with velocity , and the source appears to move with velocity . Show that the frequency received by the observer is:
The sun rotates about its axis with a period that may be assumed to be constant at . The radius of the sun is . Discuss the shifts in the frequency of light emitted from the Sun's equator and received on earth. Assume that the sun emits monochromatic light of wavelength .
In a binary star system, two stars orbit a common point and move so that they are always in diametrically opposite positions. Light from both stars reaches an observer on earth. Assume that both stars emit light of wavelength .
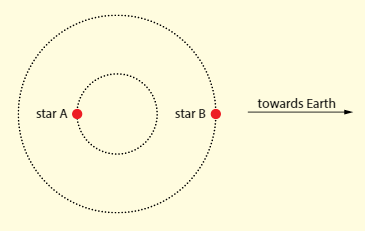
a. When the stars are in the position shown in the diagram, the observer on earth measures a wavelength of light of from the stars. Explain why there is no Doppler shift in this case.
In a binary star system, two stars orbit a common point and move so that they are always in diametrically opposite positions. Light from both stars reaches an observer on earth. Assume that both stars emit light of wavelength .
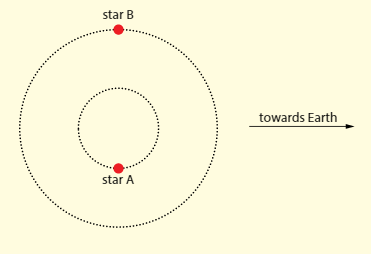
b. When the stars are in the position shown in the diagram, the observer on earth measures wavelengths in the received light and . Determine the speed of each stars.
