K K Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Motion, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
K K Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - K K Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Motion, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Rotational Motion, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Mechanis II NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K K Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Motion, Exercise 1: TOPICWISE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
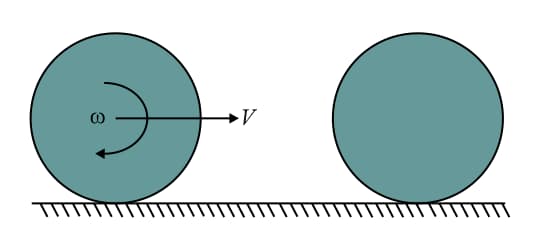
A solid sphere is rolling without slipping on a rough ground as shown in figure. It collides elastically with an identical another sphere at rest. There is no friction between the two spheres. Radius of each sphere is and mass is . The linear velocity of first sphere after it again starts rolling without slipping is,
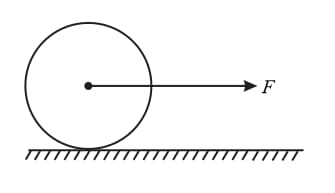
A horizontal force acts on the sphere at its centre as shown. The coefficient of friction between ground and sphere is . The value of for which there is no slipping will be,
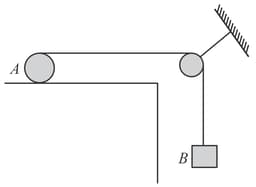
A solid cylinder of mass is being pulled by another weight () along the horizontal plane as shown in the figure (pulley is massless). The weight is attached to the end of a string wound around the circumference of the cylinder. If there is no slipping anywhere and the string is inextensible, then find acceleration (in ) of .
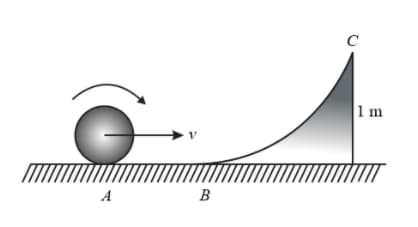
A small sphere of mass is rolling without slipping on a stationary base with linear speed, . Find its linear speed at point . ( Take .)
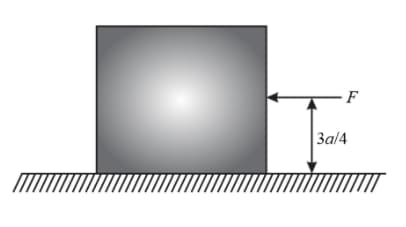
A uniform cube of side and mass rests on a rough horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied normal to one of the faces at a point that is directly above the centre of the face at a height above the base. The minimum value of for which the cube begins to topple about an edge is (assume that cube does not slide),
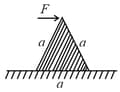
An equilateral prism of mass rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction . A horizontal force is applied on the prism as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the prism does not slide before toppling, then the minimum force required to topple the prism is,
A uniform cube of mass and side is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force, is applied to the edge as shown in figure. The normal reaction effectively acts at a distance,
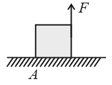
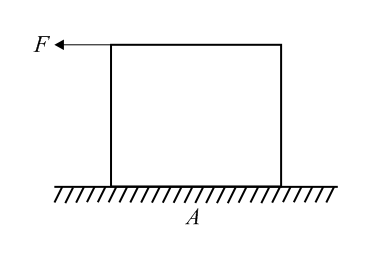
A force is applied on the top of a cube as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the cube and ground is . If is gradually increased, the cube will topple before sliding. Then, the range of is,