M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Areas Related to Circles, Exercise 1: Exercise 13.1
M L Aggarwal Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Areas Related to Circles, Exercise 1: Exercise 13.1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 13: Areas Related to Circles, Exercise 1: Exercise 13.1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CBSE Syllabus Standard Mathematics for Class X solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Areas Related to Circles, Exercise 1: Exercise 13.1 with Hints & Solutions
Find the circumference of the circle (in ) whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of three circles with radii and .
If the difference between the circumference and the radius of the circle is , then calculate the circumference of the circle (in ).
A circular park is surrounded by a road wide. If the radius of the park is , the area of the road is . Find the value of .
The wheel of a cart is making revolutions per second . If the diameter of the wheel is , then find its speed in .
A road wide surrounds a circular plot whose circumference is . Find the cost of paving the road at .
The area enclosed between two concentric circles is . If the circumference of the inner circle is , then find the radius of the outer circle.
The area of a circular ring enclosed between two concentric circles is . Find the radii of the two circles if their difference is .
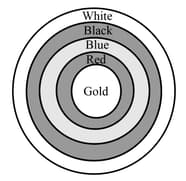
The figure shows an archery target marked with its five scoring areas from the centre outward as Gold, Red, Blue, Black and White. The diameter of the region representing Gold is and each of the other band is wide. Find the area of each of the five scoring regions.