Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Electrons and Photons, Exercise 2: Critical Thinking
Umakant Kondapure Physics Solutions for Exercise - Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Electrons and Photons, Exercise 2: Critical Thinking
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 11: Electrons and Photons, Exercise 2: Critical Thinking with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MHT-CET TRIUMPH Physics Multiple Choice Questions Part - 2 Based on Std. XI & XII Syllabus of MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Electrons and Photons, Exercise 2: Critical Thinking with Hints & Solutions
The curve for a photocell is best represented by the figure.
If and are stopping potentials for incident photons of wavelengths and for same cathode material, then Planck's constant is given by charge on the electron, speed of light]
Ultraviolet radiation of falls on an aluminium surface of work function . The kinetic energy in , of the fastest electron emitted is approximately
Choose the graph showing the correct relationship between the stopping potential and the frequency of light for potassium and tungsten.
Two identical photo-cathodes receive the light of frequencies and If the velocities of the photoelectrons (of mass ) coming out are respectively and , then:-
The stopping potential versus frequency (v) plot of a substance is shown in figure. The threshold wavelength is
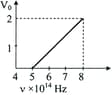
Assertion: If the maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted by a photocell is , then the stopping potential is .
Reason: Stopping potential for the fastest photoelectrons is numerically equal to their kinetic energy.
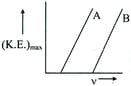
Assertion: From the graph above, it follows that the work function of metal is greater than that of metal . Reason: The work function depend upon the slope of the graph.
