Genetic Disorders
Important Questions on Genetic Disorders
Describe the individual having chromosomal abnormalities XXY.
Describe the individuals having chromosomal abnormalities XO.
Define aneuploidy. How is it different from polyploidy? Describe the individuals having trisomy of the 21st chromosome.
A normal visioned woman, whose father is colour blind, marries a normal visioned man. What would be the probability of her sons and daughters to be colour blind? Explain with the help of a pedigree chart.
It is said, that the harmful alleles get eliminated from population over a period of time, yet sickle cell anaemia is persisting in human population. Why?
If a father and son are both defective in red-green colour vision, is it likely that the son inherited the trait from his father? Comment.
Why is the frequency of red-green colour blindness is many times higher in males than that in the females?
What is Down's syndrome? Give its symptoms and cause. Why is it that the chances of having a child with Down's syndrome increases if the age of the mother exceeds forty years?
The pedigree chart given below shows a particular trait which is absent in parents but present in the next generation irrespective of sexes. Draw your conclusion on the basis of the pedigree.
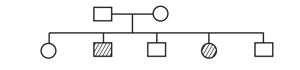
The inheritance pattern of a gene over generations among humans is studied by the pedigree analysis. Character studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to
In the sickle cell anaemia, glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following are triplets codes for valine?
If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some male progeny, the disease is
Conditions of a karyotype 2n+1, 2n-1 and 2n+2, 2n-2 are called

