Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Important Questions on Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Match the following species with their corresponding ground state electronic configuration.
| Atom/Ion | Electronic Configuration | ||
| (i) | (a) | ||
| (ii) | (b) | ||
| (iii) | (c) | ||
| (iv) | (d) | ||
| (e) | |||
Match species given in Column I with the electronic configuration given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | (a) | ||
| (ii) | (b) | ||
| (iii) | (c) | ||
| (iv) | (d) | ||
| (e) | |||
Calculate the energy and frequency of the radiation emitted when an electron jumps from to in a hydrogen atom.
The effect of uncertainty principle is significant only for motion of microscopic particles and is negligible for the macroscopic particles. Justify the statement with the help of a suitable example.
Table-tennis ball has a mass and a speed of . If speed can be measured within an accuracy of , what will be the uncertainty in speed and position?
According to de Broglie, the matter should exhibit dual behaviour, that is both particle and wave-like properties. However, a cricket ball of mass does not move like a wave when it is thrown by a bowler at a speed of . Calculate the wavelength of the ball and explain why it does not show wave nature.
The electronic configuration of the valence shell of is and not . How is the configuration explained?
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their value. Lower the value of , lower is the energy. For orbitals having the same values of , the orbital with the lower value of will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the question given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the highest energy?
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their value. Lower the value of , lower is the energy. For orbitals having the same values of , the orbital with the lower value of will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the question given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form ion. The atomic number of nickel is . From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons.
In which of the following pairs, the ions are isoelectronic?
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers are correct?
For the electrons of an oxygen atom, which of the following statements is correct?
The pair of ions having same electronic configuration is _____.
Orbital angular momentum depends on _____.
Total number of orbitals associated with third shell will be _____.
Which of the following is responsible to rule out the existence of definite paths or trajectories of electrons?
The number of angular nodes for orbital is _____.
The number of radial nodes for orbital is _____.
The probability density plots of orbitals are given in Figure
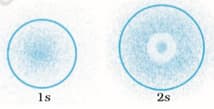
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of the above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?

