Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
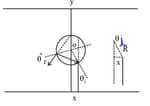
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium ) into such a medium (medium ) shall follow a path given by
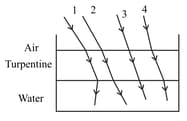
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure given below shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is . If the refractive index of the material of the lens be , it will
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed and stops at the focus. The Image
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is
An infinitely long cylinder of radius is made of an unusual exotic material with refractive index –1 (Figure). The cylinder is placed between two planes whose normals are along the direction. The centre of the cylinder lies along the -axis. A narrow laser beam is directed along the direction from the lower plate. The laser source is at a horizontal distance from the diameter in the direction. Find the range of such that light emitted from the lower plane does not reach the upper plane.
If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interaction causes a bending of the ray. This can be thought of as happening due to a change in the effective refractive index of the medium given by
where is the distance of the point of consideration from the centre of the mass of the massive body, is the universal gravitational constant, the mass of the body and the speed of light in vacuum. Considering a spherical object find the deviation of the ray from the original path as it grazes the object.
The mixture of a pure liquid and a solution in a long vertical column (i.e, horizontal dimensions vertical dimensions) produces diffusion of solute particles and hence a refractive index gradient along the vertical dimension. A ray of light entering the column at right angles to the vertical has deviated from its original path. Find the deviation in travelling a horizontal distance , the height of the column.
Show that for a material with refractive index , light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
Three immiscible liquids of densities and refractive indices are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is . A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought closer to the eye than the normal near point. This results in
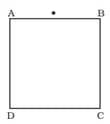
A rectangular block of glass has a refractive index . A pin is placed midway on the face (Figure). When observed from the face . the pin shall