NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 3: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
NCERT Science Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 3: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 3: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Science - Class 6 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 3: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
An electric bulb is connected to a cell through a switch as shown in figure. When the switch is brought in ‘ON’ position, the bulb does not glow. What could be the possible reason/s for it? Mention any two of them.

A torch requires cells. Show the arrangement of the cells, with a diagram, inside the torch so that the bulb glows.
When the chemicals in the electric cell are used up, the electric cell stops producing electricity. The electric cell is then replaced with a new one. In case of rechargeable batteries (such as the type used in mobile phones, camera and inverters), they are used again and again. How?
Paheli connected two bulbs to a cell as shown in figure.
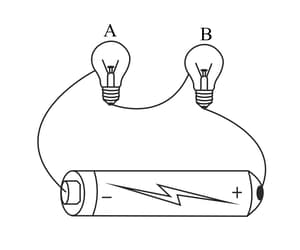
She found that filament of bulb B is broken. Will the bulb A glow in this circuit? Give reason.
Why do bulbs have two terminals?
Which of the following arrangement A, B, C and D given in figure should not be set up? Explain, why.




A fused bulb does not glow. Why?
Paheli wanted to glow a torch bulb using a cell. She could not get connecting wires, instead, she got two strips of aluminium foil. Will she succeed? Explain, how?
