NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Short Answer Type
NCERT Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Short Answer Type
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Short Answer Type with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Chemistry - Class 11 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Short Answer Type with Hints & Solutions
The enthalpy of vapourisation of is . Calculate the heat required for the vapourisation of of at constant pressure. (Molar mass of ).
The enthalpy of reaction for the reaction:
is . What will be standard enthalpy of formation of ?
What will be the work done on an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder, when it is compressed by a constant external pressure, in a single step as shown in Figure? Explain graphically.
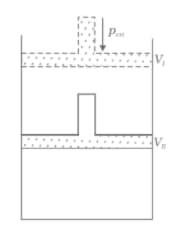
How will you calculate work done on an ideal gas in a compression, when change in pressure is carried out in infinite steps?
Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following processes graphically.
(a) Throwing a stone from the ground to roof.
(b)
In which of the processes potential energy/enthalpy change is contributing factor to the spontaneity?
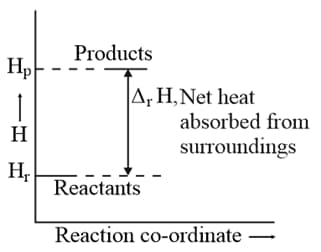
Enthalpy diagram for a particular reaction is given in Figure. Is it possible to decide spontaneity of a reaction from given diagram? Explain.
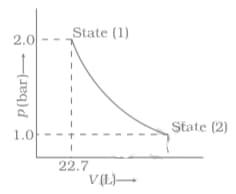
mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state () to state () as shown in Figure. Calculate the work done for the expansion of gas from state () to state () at .
An ideal gas is allowed to expand against a constant pressure of bar from to in one step. Calculate the amount of work done by the gas. If the same expansion were carried out reversibly, will the work done be higher or lower than the earlier case? (Given that )
