NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Mechanical Properties of Solids, Exercise 5: LA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Mechanical Properties of Solids, Exercise 5: LA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Mechanical Properties of Solids, Exercise 5: LA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 11 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Mechanical Properties of Solids, Exercise 5: LA with Hints & Solutions
A steel wire of mass per unit length with a circular cross-section has a radius of The wire is of length when measured lying horizontal, and hangs from a hook on the wall. A mass of is hung from the free end of the wire. Assuming the wire to be uniform and the lateral strains longitudinal strains, find the extension in the length of the wire. The density of steel is (Young's modules )
A steel wire of mass per unit length with a circular cross-section has a radius of The wire is of length when measured lying horizontal, and hangs from a hook on the wall. A mass of is hung from the free end of the wire. Assuming the wire to be uniform and the lateral strains longitudinal strains,. The density of steel is . If the yield strength of steel is, what is the maximum weight that can be hung at the lower end of the wire?
A steel rod of length cross-sectional area and mass is set rotating in a horizontal plane about an axis passing through the center. If is Young's modulus for steel, find the extension in the length of the rod. (Assume the rod is uniform)
An equilateral triangle is formed by two Cu rods and and one rod. It is heated in such a way that temperature of each rod increases Find change in the angle [Coefficient of linear expansion for is ], coefficient of linear expansion for is ].
In nature, the failure of structural members usually results from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus, the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by
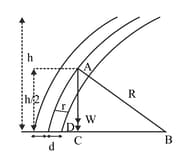
is Young's modulus, is the radius of the trunk and is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along with the height of the tree containing the center of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
A stone of mass is tied to an elastic string of negligible mass and spring constant . The unstretched length of the string is and has negligible mass. The other end of the string is fixed to a nail at a point Initially the stone is at the same level as the point . The stone is dropped vertically from point Find the distance from the top when the mass comes to rest for an instant, for the first time.
A stone of mass is tied to an elastic string of negligible mass and spring constant . The unstretched length of the string is and has a negligible mass. The other end of the string is fixed to a nail at a point Initially the stone is at the same level as the point . The stone is dropped vertically from point. What is the maximum velocity attained by the stone in this drop?
A stone of mass is tied to an elastic string of negligible mass and spring constant . The unstretched length of the string is and has negligible mass. The other end of the string is fixed to a nail at a point Initially the stone is at the same level as the point . The stone is dropped vertically from point What shall be the nature of the motion after the stone has reached its lowest point?
