NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 5: LA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 5: LA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 5: LA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 11 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 5: LA with Hints & Solutions
A block of mass is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30" by a force of parallel to the inclined surface (figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is If the block is pushed up by along the incline, calculate
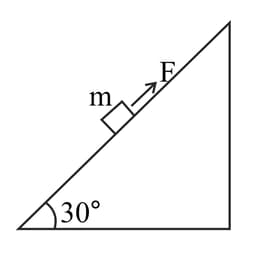
(d) increase in kinetic energy
A block of mass is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30" by a force of parallel to the inclined surface (figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is If the block is pushed up by along the incline, calculate
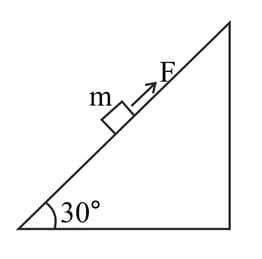
(e) work done by applied force.
A curved surface is shown in figure. The portion is free of friction. There are three spherical balls of identical radii and masses. Balls are released from rest one by one from A which is at a slightly greater height than . With the surface , ball has large enough friction to cause rolling down without slipping; ball has a small friction and ball has a negligible friction.
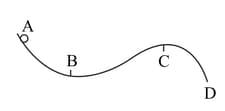
(a) For which ball is total mechanical energy conserved?
A curved surface is shown in figure. The portion is free of friction. There are three spherical balls of identical radii and masses. Balls are released from rest one by one from A which is at a slightly greater height than . With the surface , ball has large enough friction to cause rolling down without slipping; ball has a small friction and ball has a negligible friction.
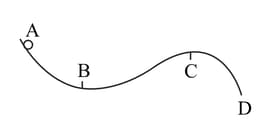
(b) Which ball can reach ?
A curved surface is shown in figure. The portion is free of friction. There are three spherical balls of identical radii and masses. Balls are released from rest one by one from A which is at a slightly greater height than . With the surface , ball has large enough friction to cause rolling down without slipping; ball has a small friction and ball has a negligible friction.
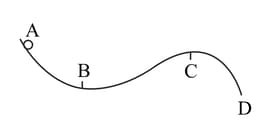
(c) For balls which do not reach , which of the balls can reach back ?
A rocket accelerates straight up by ejecting gas downwards. In a small time interval it ejects a gas of mass at a relative speed . Calculate of the entire system at and and show that the device that ejects gas does work in this time interval (neglect gravity).
Two identical steel cubes (masses , side 1cm) collide head-on face to face with a speed of each. Find the maximum compression of each. Young's modulus for steel .
A balloon filled with helium rises against gravity increasing its potential energy. The speed of the balloon also increases as it rises. How do you reconcile this with the law of conservation of mechanical energy? You can neglect viscous drag of air and assume that density of air is constant.
