NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Is Matter Around Us Pure?, Exercise 1: Exercise
NCERT Science Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Is Matter Around Us Pure?, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Science Textbook of Competency Based Questions for Class IX solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Is Matter Around Us Pure?, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
Tina passes a light beam through two liquid mixtures in separate glasses.
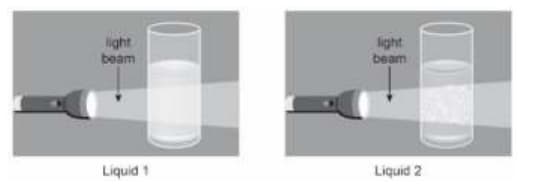
Based on the behaviour of the light beam what are liquid and .
Tina passes a light beam through two liquid mixtures in separate glasses.
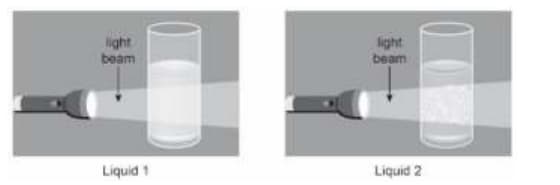
Which of these is true about the particles in the two liquids?
Which of these is an alloy?
Which of these is common for all chemical changes?
| Is it shiny? | How does it conduct electricity? | |
| Substance | yes | very good |
| Substance | no | very good |
| Substance | yes | medium |
| Substance | no | poor |
Which substance is most likely to be a metalloid?
A gas cylinder has the following symbol on its surface.

Which property of the gas is represented by the symbol?
Characteristic reactions for four different substances are given below. Arrange the tests in the order of the substances given below.
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)-
Passage through potassium dichromate turns green.
-
Dissolution in water gives a tribasic acid.
-
Non-supporter of combustion but allows active metals to continue to burn.
-
Turns alkaline pyrogallol brown.
Colour changes observed during the reaction between metal oxides and hydrogen are given below:
(1) white bluish white
(2) brown grey
(3) yellow grey
(4) black red
Arrange the above colour changes as to , to , to and to .
