Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: Electricity, Exercise 4: MOCK TEST QUESTION PAPER
Neha Jindal Physics Solutions for Exercise - Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: Electricity, Exercise 4: MOCK TEST QUESTION PAPER
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 3: Electricity, Exercise 4: MOCK TEST QUESTION PAPER with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. SCIENCE PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: Electricity, Exercise 4: MOCK TEST QUESTION PAPER with Hints & Solutions
State one condition on which resistivity of a metal depends.
State the relation between works, charge and potential difference for an electric circuit. Calculate the potential difference between the two terminals of a battery if of work is required to transfer of charge from one terminal of the battery to the other.
What is Joule’s heating effect? How can it be demonstrated experimentally? List its four applications in daily life
Explain with the help of a labelled circuit diagram, how you will find the resistance of a combination of three resistors, of resistance , joined in parallel. Also mention how you will connect the ammeter and the voltmeter in the circuit when measuring the current in the circuit and the potential difference across one of the three resistors of the combination.
What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is ? Name a device that helps to measure the potential difference across a conductor.
Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow hot while the heating element does?
Electrical resistivity of some substances at are given below
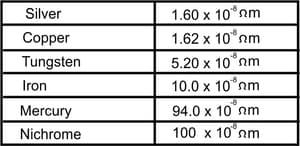
| Silver | |
| Copper | |
| Tungsten | |
| Iron | |
| Mercury | |
| Nichrome |
Answer the following questions in relation to them:
(i) Among silver and copper, which one is a better conductor? Why? (ii) Which material would you advise to be used in electrical heating devices? Why?
Find out the following in the electric circuit given in figure:
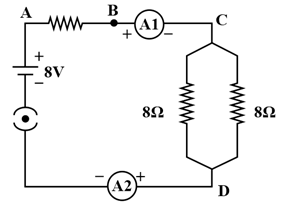
(a) Effective resistance of two resistors in the combination,
(b) Current flowing through resistor,
(c) Potential difference across resistance,
(d) Power dissipated in resistor, and
(e) Difference in ammeter readings, if any.
