Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and The Colourful World, Exercise 1: Progress Check 1
Neha Jindal Physics Solutions for Exercise - Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and The Colourful World, Exercise 1: Progress Check 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: The Human Eye and The Colourful World, Exercise 1: Progress Check 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. SCIENCE PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Neha Jindal Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and The Colourful World, Exercise 1: Progress Check 1 with Hints & Solutions
The following table lists a few functions/phrases/statements in column . Match these items in column to the corresponding terms in column . Note that more than one item in column may match with the same item in column .
| Column | Column |
| A1 Light-sensitive screen | B1 Hypermetropia |
| A2 Cells on this part generate electrical signals upon illumination | B2 Retina |
| A3 Near-sightedness | B3 Deviation |
| A4 Corrected by using bifocal lenses | B4 Myopia |
| A5 Inability to see nearby objects clearly | B5 Ciliary muscles |
| A6 With objects at , the image is formed behind the retina | B6 Increased focal length of the eye-lens |
| A7 Modify the curvature of the eye-lens | B7 Presbyopia |
| A8 Milky and cloudy eye-lens | B8 Cataract |
| A9 Near point of the eye moves away | B9 Reddish colour of the sky |
| A10 Distance of the far point decreases | B10 Scattering of light |
| A11 Corrected by a converging lens | B11 Refraction |
| A12 Corrected by a concave lens | B12 Scattering of light |
| A13 Relaxed ciliary muscles | B13 Twinkling of stars |
| A14 Difficulty in reading blackboard while sitting in the last row | B14 Spectrum |
| A15 Caused by excessive curvature of the eye lens | B15 Increase in size of the eye-ball |
| A16 Caused by increased focal length of the eye lens | B16 Decrease in size of the eye-ball |
| A17 Caused by light passing through thinner layers of air | |
| A18 Makes the sky appear bluish | |
| A19 The band of coloured components of white light | |
| A20 The phenomenon causing advancing sunrise and delayed sunset | |
| A21 Caused by changing physical conditions of the atmosphere | |
| A22 Angle formed between the incident ray and the emergent ray in a prism |
A few defects of the human eye and the functions/relevant definition, information about different parts of the-human eye are listed in columns and below. Select the pairs, in the two columns that match each other.
| Column | Column |
| A1 The human eye | B1 regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye |
| A2 Automatic accommodation of the eye | B2 delicate membrane with very large number of light sensitive cells |
| A3 Retina | B3 behaves like a photographic camera |
| A4 Ciliary muscles | B4 Inability to see nearby objects clearly |
| A5 Myopia | B5 Carry electrical signal generated by the image to the brain |
| A6 Cataract | B6 Dark muscular diaphragm which controls the size of the pupil |
| A7 Presbyopia | B7 milky and cloudy crystalline lens of the eye |
| A8 Iris | B8 ability of eye to see objects, between to infinity, clearly |
| A9 Pupil | B9 increase or decrease in the curvature of the eye lens |
| A10 Optic nerves | B10 for object at infinity, the image is formed in front of the retina |
| A11 Far sightedness | B11 decreased power of accommodation due to old age |
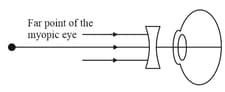
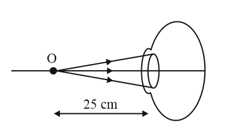
Complete each of the following diagrams to show the image formation. The nature of the eye, normal/myopia/hypermetropia is indicated with each diagram.
A. Normal eye, object at from the eye lens
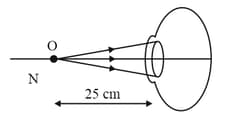
B. Hypermetropic eye, object at from the eye lens
C. Myopic eye, object at infinity
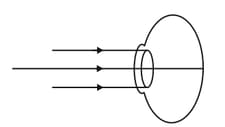
D. Hypermetropic eye
E. Myopic eye