Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
Important Questions on Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
The variation of the resistance of a metallic conductor with temperature is shown in Fig.
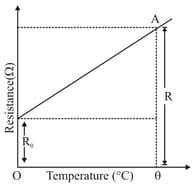
State why the resistance of the conductor increases with the rise in temperature.
The variation of the resistance of a metallic conductor with temperature is shown in Fig.
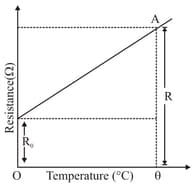
Calculate the temperature coefficient of resistance from the graph.
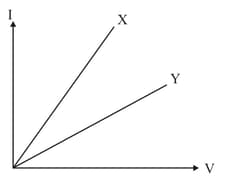
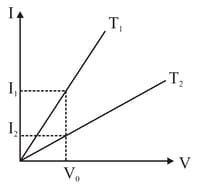
The voltage-current variation of two metallic wires and at constant temperature are shown in Fig. Assuming that the wires have the same length and the same diameter, explain which of the two wires will have larger resistivity.
- graph for a metallic wire at two different temperatures, and is as shown in Fig. 3.256. Which of the two temperatures is lower and why?
Choose the correct alternative:
The resistivity of a semiconductor increases/decreases rapidly with increasing temperature.
Choose the correct alternative:
The resistance of graphite and most nonmetals increases/decreases with increase in temperature.
Choose the correct alternative:
Doping a semiconductor (with small traces of impurity atoms) reduces/increases its resistivity.
Answer the following questions:
In which respect, does a nearly discharged lead-acid secondary cell differ mainly from a freshly charged cell in its emf or in its internal resistance?
Answer the following questions:
It is easier to start a car engine on a warm day than on a chilly day. Why?
Answer the following questions:
It is easier to confine electric current to definite paths (by the use of electric insulators) than to direct heat flow along definite routes using heat insulators. Why?
Two materials and (or and ) are cooled from to . What will be the effect on their resistivity?
Why does the conductivity of a semiconductor increase with rise of temperature?
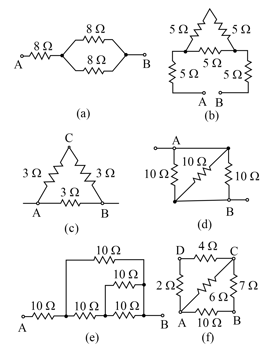
Letter as shown in Fig. has resistances on each side of arm. Calculate the total resistance between two ends of the legs.
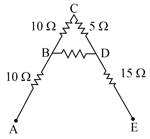
Find the equivalent resistance between points and in Fig.
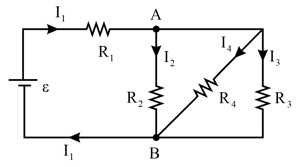
In the circuit shown in Fig, and . Work out the equivalent resistance of the circuit and the current in each resistor.
In the circuit diagram shown in Fig. voltmeter reads when connected across resistance. Calculate what the same voltammeter reads when it is connected across resistance.
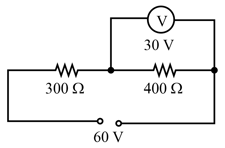
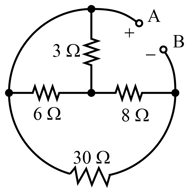
Find the potential difference between the point and for the network shown in Fig.
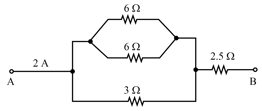
Find the equivalent resistance of the networks shown in Fig. between the points and
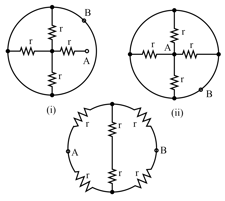
Calculate the resistance between points and for the following networks:
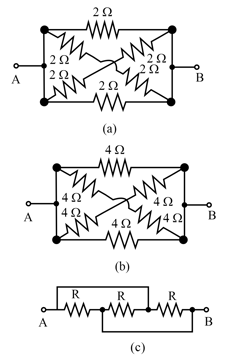
Calculate the equivalent resistance between points and in each of the following networks of resistors: