Electrostatic Potential and Potential Difference
Important Questions on Electrostatic Potential and Potential Difference
Name the machine which makes use of this principle. Draw a simple labelled line diagrams of this machine. What’s ‘practicle difficulty’ puts on upper linit on the maximum potential difference which this machine can built up?
Express the unit of electric potential in terms of the base units of SI.
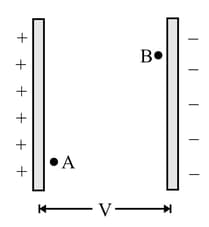
Two protons and are placed between two parallel plates having a potential difference , as shown in figure below. Will these protons experience equal or unequal force?
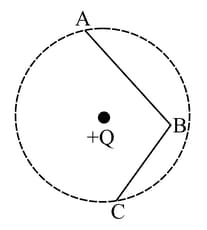
In the figure below charge is placed at the centre of a dashed circle. Work done in taking another charge from to is and from to is . Which one of the following is correct: and ?
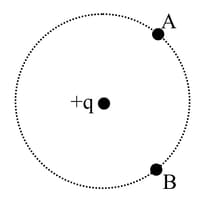
What would be the work done if a point charge , is taken from a point to the point on the circumference of a circle with another point charge at the centre?
A positive charge is located at a point. What is the work done if a unit positive charge is carried once round this charge along a circle of radius about this point.
Can there be a potential difference between two neighbouring conductors carrying equal positive charges?
Two point charges of and are placed in free space apart. Find the electric potential at the middle point of the line joining the two charges.
A hollow metal sphere is charged with of charge and has a radius of . Find the potential at a distance of from the centre. The sphere is placed in air.
A hollow metal sphere is charged with of charge and has a radius of . Find the potential inside the surface.
A hollow metal sphere is charged with of charge and has a radius of . Find the potential at the surface.
Two points and are located in diametrically opposite directions of a point charge of at distances and respectively from it. Determine the potential difference .
The electric field at a point due to a point charge is and the electric potential at that point is . Calculate the distance of the point from the charge and the magnitude of the charge.
The electric potential at from a point charge is . What is the magnitude and sign of the charge?
A small sphere of radius and charge is enclosed by a spherical shell of radius and charge Show that if is positive, charge will necessarily flow from the sphere to the shell (when the two are connected by a wire) no matter what the charge on the shell is.
Guess a possible reason why water has a much greater dielectric constant than say, mica
We know that electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a charged conductor. Is electric potential also discontinuous there?
What is the work done by the field of a nucleus in a complete circular orbit of the electron? What if the orbit is elliptical?
A small test charge is released at rest at a point in an electrostatic field configuration. Will it travel along the field line passing through that point?
If Coulomb’s law involved dependence (instead of ), would Gauss’s law be still true?

