S. L. Arora Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current and Electrical Machines, Exercise 3: Problems For Practice
S. L. Arora Physics Solutions for Exercise - S. L. Arora Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current and Electrical Machines, Exercise 3: Problems For Practice
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Alternating Current and Electrical Machines, Exercise 3: Problems For Practice with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS A Reference Book for Class 12 Volume 2 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from S. L. Arora Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current and Electrical Machines, Exercise 3: Problems For Practice with Hints & Solutions
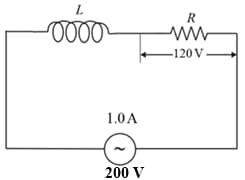
The virtual current in the a.c. circuit shown in Figure, is . Find (i) virtual voltage across the coil (ii) impedance of the circuit and (iii) reactance of the coil.
A circuit containing a resistance of and an inductance of H in series is connected to a a.c. line of frequency . Find the reactance, the impedance, the current in the circuit and the phase difference between the alternating voltage and current.
An a.c. circuit consists of a supply connected across a resistor. What inductance should be connected in the circuit in series with resistance so that the current is reduced to half?
A long solenoid connected to a d.c. source passes a steady current of When the solenoid is connected to an a.c. source of at , the current flowing is . Calculate the inductance of the solenoid.
A choke coil and a resistance are connected in series in an a.c. circuit. A potential difference of is applied to the circuit. If the potential difference across the resistance is , what should be the potential difference across the choke coil?
An emf, volt is applied across an inductance having a resistance of . The maximum current is found to be . Find the value of .
An electric circuit containing an inductance and resistance in series has an impedance of at and an impedance of at . Find the values of and .
In the RL-circuit shown in figure, resistance , reactance and peak emf .
Calculate the (i) impedance (ii) phase difference between the emf and current and (iii) the peak current in the circuit.
