NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 3: Current Electricity, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS PART-1 TEXTBOOK FOR CLASS XII solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
What conclusion can you draw from the following observations on a resistor made of alloy manganin?
| Current A | Voltage V | Current A | Voltage V |
|---|---|---|---|
A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. Which of these qualities is constant along the conductor: current, current density, electric field, drift speed?
Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
A high tension (HT) supply of, say, must have a very large internal resistance. Why?
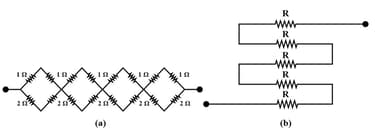
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown below.
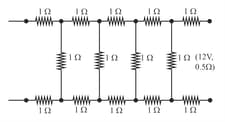
Determine the current drawn from a supply with internal resistance by the infinite network shown below. Each resistor has resistance
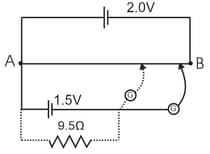
The figure shows a potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is . When a resistor of is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.