NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electric Charges and Fields, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electric Charges and Fields, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS PART-1 TEXTBOOK FOR CLASS XII solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electric Charges and Fields, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
A conductor with a cavity as shown in figure is given a charge . Show that the entire charge must appear on the outer surface of the conductor.
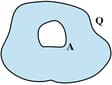
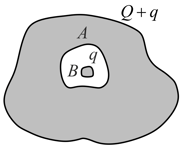
A conductor with cavity as shown in the figure is given a charge . Another conductor with charge is inserted into the cavity keeping insulated from . Show that the total charge on outside the surface of is .
A sensitive instrument is to be shielded from the strong electrostatic fields in its environment. Suggest a possible way.
A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show that the electric field in the hole is ( ) , where is the unit vector in the outward normal direction, and is the surface charge density near the hole.
Obtain the formula for the electric field due to a long thin wire of uniform linear charge density without using Gauss’s law. [Hint: Use Coulomb’s law directly and evaluate the necessary integral.]
It is now believed that protons and neutrons (which constitute nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so called ‘up’ quark (denoted by ) of charge and the ‘down’ quark (denoted by ) of charge together with electrons build up ordinary matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark composition of a proton and neutron.
Consider an arbitrary electrostatic field configuration. A small test charge is placed at a null point (i.e., where ) of the configuration. Show that the equilibrium of the test charge is necessarily unstable. Verify this result for the simple configuration of two charges of the same magnitude and sign placed a certain distance apart.
A particle of mass and charge enters the region between the two charged plates initially moving along -axis with speed .The length of plate is and an uniform electric field is maintained between the plates.
(a) Show that the vertical deflection of the particle at the far edge of the plate is Compare this motion with motion of a projectile in gravitational field.
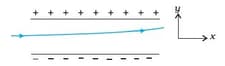
(b) Suppose that the particle is an electron projected with velocity . If between the plates separated by is where will the electron strike the upper plate?
