Chemical Properties of Metals
Chemical Properties of Metals: Overview
This topic describes the chemical properties of metals. It explains that metals form basic oxides when they react with oxygen and form salt and hydrogen gas on reacting with acids.
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Metals
SOLVE THE PUZZLE
CLUES
Across:
4. Another word for type of shininess.
7. Mixture of two or more different metals.
8. This metal is not malleable.
12. Property which allows material to bend when hit with a hammer.
14. Luster that is shown by a piece of wood or graphite.
16. Glass and wood are examples.
17. Material reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
18. Luster that is shown by glass.
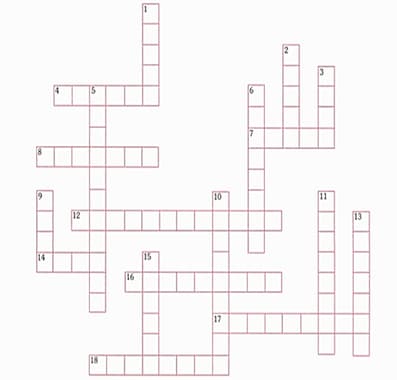
Down :
1. This property is least useful in telling if something is a metal.
2. Copper, Zinc and Tin are examples of this.
3. Luster that is shown by a candle.
5. Lead may be said to have this luster.
6. This non-metal, a form of Carbon, conducts electricity.
9. This precious metal does not oxidise.
10. These are free to move in metals but are held in place in non-metals.
11. Zinc has this luster.
13. This non-metal, a precious form of Carbon, does not conduct electricity.
15. This metal forms the outside of pennies.
Of these, the most reactive metal is:
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings?
On heating ferrous sulphate crystals, one would get
When you place iron nail in copper sulphate solution, the reddish-brown coating formed on the nail is
The colour of and formed when lead nitrate is heated are
of freshly prepared iron sulphate was taken in each of four test tubes. Strips of copper, iron, zinc and aluminium were introduced in a different test tube. A black residue was obtained in two of them. The right pair of metals forming the precipitates is
The colour of calcium oxide is
Which one is an alkali amongst the chemicals given below?
The precipitate of barium sulphate formed by the reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution is soluble in:
Four test tubes were taken and marked A, B, C and D respectively. mL of solution of in water was filled in each of the four test tubes. Clean piece of zinc was placed in test tube A, clean iron nail was put in test tube B, clean copper wire was placed in test tube C and a clean aluminium wire was placed in test tube D. It was observed that no change occurs in any of the test tubes. The correct inference drawn is:
Which of the following statement is not correct for the following reaction?
Pieces of zinc metal are added to four different test tubes containing different solutions, in which test tube no change will be observed?
When an aluminium strip is kept immersed in freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution taken in a test tube, the change which is observed is
Four students of a practical group a, b, c, d were assigned the experiment of reaction of iron nails with copper sulphate separately, which one of the students of group recorded all the correct observations.
Student Initial colour of solution. Final colour of solution.
A student added dil. to a test tube containing granules and made following observations:
(i) Zinc surface become dull and black.
(ii) A gas evolved which burn with a pop sound.
(iii) The solution remained colourless.
What is the correct chemical name of ?
What is the form of Zinc metal available for performing experiment in the laboratory.
Zinc metal shows amphoteric nature, it is due to which one of the following facts:
Which of the chemical reaction represents the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid.
