Faraday's Law of Induction
Important Questions on Faraday's Law of Induction
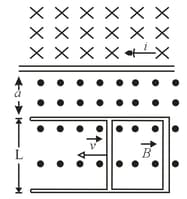
Figure shows, a rod of length that is forced to move at constant speed of along the horizontal rails. The rod, rails and connecting strip at the right form a conducting loop. The rod has resistance and the rest of the loop has negligible resistance. A current through the long straight wire at distance from the loop sets up a (non-uniform) magnetic field through the loop. Find the
(a) emf and
(b) current induced in the loop. (c) At what rate is thermal energy generated in the rod? (d) What is the magnitude of the force that must be applied to the rod to make it move at constant speed?
(e) At what rate does this force do work on the rod?
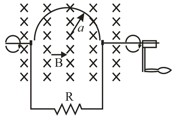
In the figure, a stiff wire bent into a semicircle of radius is rotated at constant angular speed of in a uniform magnetic field. What are the (a) frequency and (b) amplitude of the emf induced in the loop?
A -shaped conductor is located in a uniform magnetic field, perpendicular to the plane of the conductor, and varying with time at the rate . A conducting connector starts moving with an acceleration , along the parallel bars of the conductor. The length of the connector is equal to . Find the emf induced in the loop at after the beginning of the motion, if at the moment , the loop area and the magnetic induction are equal to zero. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
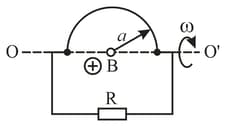
A wire shaped as a semi-circle of radius , rotates about an axis with an angular velocity , in a uniform magnetic field of induction . The rotation axis is perpendicular to the field direction. The total resistance of the circuit is equal to . Neglecting the magnetic field of the induced current, find the mean amount of thermal power being generated in the loop during a rotation period.
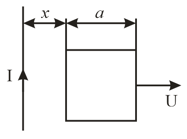
A square frame, with side , and a long straight wire, carrying a current , are located in the same plane, as shown in the figure. The frame translates to the right with a constant velocity . Find the emf induced in the frame as a function of distance .
The magnetic flux passing through a coil of turns is given by
Find out-
(a) Maximum induced emf
(b) Induced emf at time
(c) Induced current at (if external resistance is )
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loudspeaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area with closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in coil ( measured by ballistic galvanometer connected to the coil) is . The combined resistance of coil and galvanometer is . Calculate the field strength of the magnet.
A square loop of side with its sides parallel to axis is moved with a velocity in the positive direction in an environment containing magnetic field in the positive direction. The field is neither uniform in space or constant in time. It has a gradient of in the negative direction( i.e. it increases by as one moves along the -ve direction) and it is decreasing in time at the rate of . Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is .
An a.c. generator consists of a coil of turns and area rotating at an angular speed of in a uniform magnetic field of The resistance of the circuit including that of the coil is (i) Find the peak value of current drawn from the generator. (ii) What is the flux through the coil when the current is zero?
An armature coil consists of turns of wire, each of area and total resistance . It rotates in a magnetic field of at a constant frequency of . Calculate the value of (i) maximum (ii) average induced emf produced in the coil.
A rectangular wire loop of sides and with a small cut is stationary but the current feeding the electromagnet that produces the magnetic field is gradually reduced so that the field decreases from its initial value of at the rate of . If the cut is joined and the loop has a resistance of , how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat? What is the source of this power?
A circular coil of radius and turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude . Obtain the maximum and average emf induced in the coil. If the coil forms a closed loop of resistance , calculate the maximum value of current in the coil. Calculate the average power loss due to Joule heating. Where does this power come from?
A long solenoid with turns per has a small loop of area placed inside the solenoid normal to its axis. If the current carried by the solenoid changes steadily from to in , what is the induced emf in the loop while the current is changing?

