Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light
In a Geiger-Marsden experiment, what is the distance of the closest approach to the nucleus of an alpha particle before it comes momentarily to rest and reverse its direction? Given: Kinetic energy of -particle and for gold.
Does a photon carry momentum?
At atom of mass M which is in the state of rest emits a photon of wavelength . As a result, the atom will deflect with the kinetic energy equal to (h is Planck's constant)
In a photoelectric effect experiment, the slope of the graph between the stopping potential and the incident frequency will be of the order of
For light having frequency more than threshold frequency the number of electrons emitted in photo-electric effect experiment is proportional to
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength . The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength is used. Find the work function in .
Consider figure for photoemission.
How would you reconcile with momentum-conservation? Note light (photons) have momentum in a different direction than the emitted electrons.
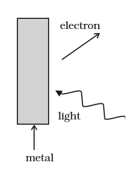
In the explanation of photo electric effect, we assume one photon of frequency collides with an electron and transfers its energy. This leads to the equation for the maximum energy of the emitted electron as
where is the work function of the metal. If an electron absorbs photons (each of frequency ), what will be the maximum energy for the emitted electron? Why is this fact (two photon absorption) not taken into consideration in our discussion of the stopping potential?
In the explanation of photoelectric effect, we assume one photon of frequency collides with an electron and transfers its energy. This leads to the equation for the maximum energy of the emitted electron as
where is the work function of the metal. If an electron absorbs photons (each of frequency ), what will be the maximum energy for the emitted electron?
Monochromatic light of frequency is produced by a laser. The power emitted is . Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source. Take
The wavelength of a spectral line is . Calculate its frequency and energy. Take, ,
