ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Jharkhand Board Physics Solutions for Exercise - ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Simple step-by-step solutions to ADDITIONAL EXERCISES questions of Current Electricity from PHYSICS PART-1 : CLASS XII. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
A high tension (HT) supply of, say, must have a very large internal resistance. Why?
Given resistors each of resistance how will you combine them to get the (i) maximum (ii) minimum effective resistance? What is the ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance?
Given the resistances of how will you combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
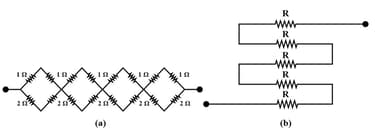
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown below.
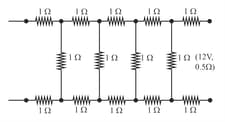
Determine the current drawn from a supply with internal resistance by the infinite network shown below. Each resistor has resistance
The figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of and internal resistance maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of (for very moderate currents up to a few ) gives a balance point at length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf , and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at length of the wire.
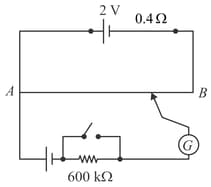
(a) What is the value ?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of instead of ?
(e) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few (such as the typical emf of a thermocouple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
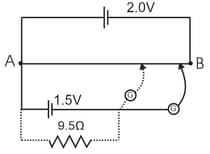
The figure shows a potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is . When a resistor of is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.